CIAutomation
II Designinh a Source control strategy with CodeCommit
-
Devops covers at least the following areas:
- Development workflows
- Test, build, and deploy applications
- Infrastructure as a code
-
Why AWS
- AWS is public cloud leader
- AWS is a full platform of integration with other services.
-
What is Devops
It is a blanket term for tooling, practices, and ideas that allow organization sto build better software - faster. It includes:
- Source control systems
- Agile software technologies
- Infrastructure as a code
- Automated testing
- Automated deployment
-
What is CI/CD
- CI= Continuous integraation. This includes:
- Commit your code to SCM
- Build your code
- Run tests
- Continuous Delivery includes all stages in CI plus the followings:
- Deploy to QA for testing
- Request manual approval
- Deploy to Production
- Continouos Deployment includes all stages mentioned before, except the “request for manaul approval "
- CI= Continuous integraation. This includes:
-
Version control systems, VCS
- Distributed VCS:
- Mercurial
- Git
- Centralised VCS
- SVN
- CVS
- Perforce
- Distributed VCS:
-
Git flow
- Complicated
- Great for maintain multiple versions of software
- Popular before web
- Github flow is well suited to web development: Vincent Driessen
-
Github flow
- Popular for web development
- Encourage best practices with frequent smaller merges
- Well suited for CI/CD practices.
-
Benefits of CodeCommit-
- You do not maintain the infra hosting your code
- user and team management
- Permission management
- Integration with CI/CD tooling and testing workflows
- Allow you code review and pull request approval workflow
-
Working with AWS CodeCommit
-
Using admin account create a CodeCommit repo
-
Add IAM user with specific permissions
-
Users can generate credentials and used them to get CodeCommit repo
-
-
How to use CodeCommit
-
Open the CodeCommit console
-
Click Create repository
-
Type repository name
-
Click Create, this will create a repo using the root account. WE need to create IAM
-
Go to the IAM console
-
Creat new user by clicking “Users”, left side
-
Type name of the user, select Programatic access and AWS management console access, click next
-
Add permissions to this user:
- You can create a group, click create group
- Enter group name, for example : developers
- Select policy:
- You can select “poweruseraccess “policy if you do not know what to choose.
- Also you can select “codecommit power user” policy
- Click create group
- Now that we have created a group, click it and it will add the user to this group
- You can add tags if you need group users.
- Click create user
NOTE: Once you click create, you will have ONLY ONE CHANGE TO copy - Secret access key - Password - Access key ID - Sigin link
**----> Copy them to a safe place**
-
-
First push to CodeCommit
- Open the Signin as IAM user page
- Enter you account ID, IAM user name, and password
- Go then to the CodeCommit console
We need to create an SSH key for the repository we will work on: - Click on the repository - Click on SSH - From you local directory, generate a pair of SSH keys. - Upload the PUBLIC key in the AIM access manager - Open AIM console - CLick on users, and find your user - Click en security credentials - CLick on “upload ssh key public” - Copy the SSH KEY ID
- Add an entry in your `.ssh/config` file with the following Host git-codecomit.*.amazonaws.com User YOUR AIM SSH KEY ID Identify ~/.ssh/id_rsa <-- private key Note: - .ssh/config permission should be 600 - Now you can clone from your local as: $ git clone ssh://git-codecommit.us-east-1.amazonaws.clm/v1/repos/test
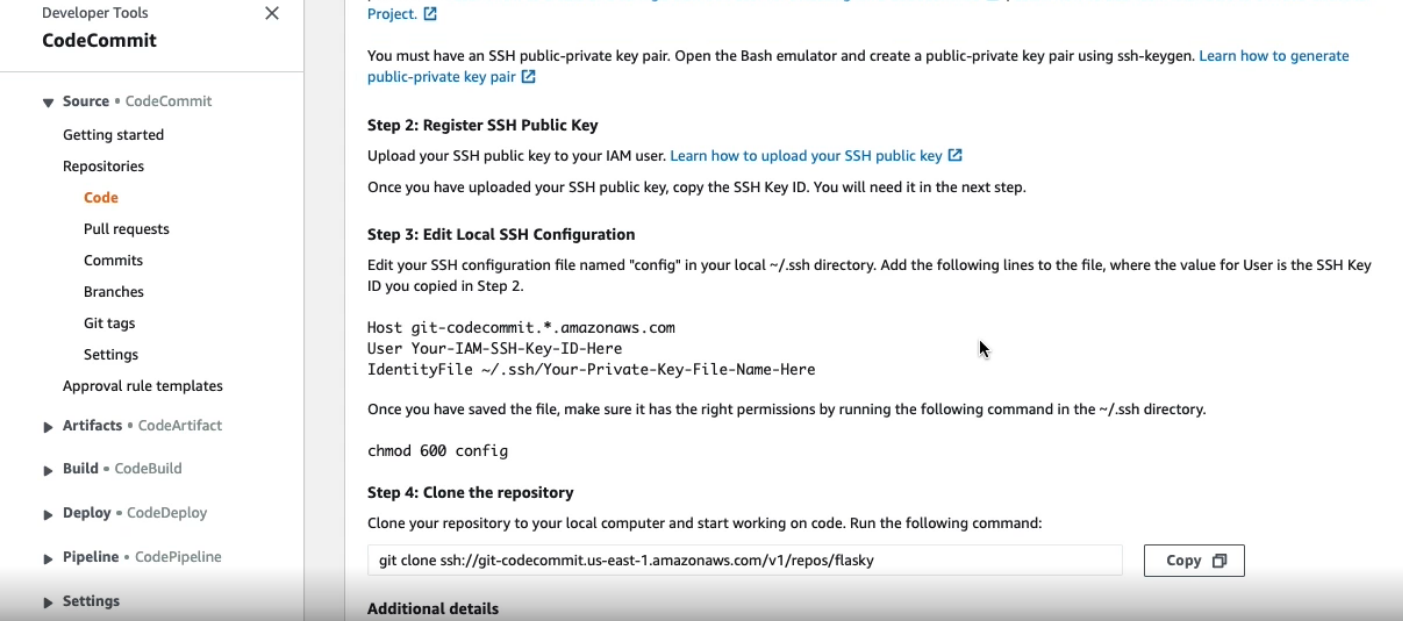
Codecommit from command line
III Infrastrcuture as a code
-
Benefits:
-
Not expensive, cost management
- You can allocate cost for all resources. For example by tagging the resource
- You can have stimated costs for each stack
- Helps you to avoid leftover resources
- Offers policy compliance
- Less redundant work
-
Reproducible
- No UI to make mistakes in
- No series of commands to run correctly
- Use one config file and deploy
- Parametrize across different regions or stages
-
Secure
- Templates can be reviewed by other developers
- Create approved reusable templates
- Limit the way of changing infra
- Audits can focus on IaC changs and app logs
-
-
AWS cloud formation
-
What is?
- AWS service to manage infra as a code
- Uses Json or Yaml syntax
- Allows extend through AWS Lambda
- Controls the state of your infra by describing every single cloud resource in code
-
Basic concepts
- Templates: Information about the resources to create
- Stacks: List of AWS resources to create using templates
- AWS Resources
-
Tools
- AWS CDK
- AWS SAM
- £rd party frameworks
-
AWS cloud development kit
- Controling your infra using high-level or low-level constructs that consist of one or more cloud resources.
-
AWS serverless application model: LAMBDA
- Developing and deploying AWS lambda based applications
-
AWS code deploy
- Deploying application code to different cpmpute services with nuanced rollout strategies.
-
Permissions
- Need to set permission to work with CloudFormation
- Also permissions for all the services touched by CLoudFormation
-
Security for CloudFormation with CI/CD
- Build pipelines using CLoudFormation carry lots of permissions
- Have isolated and inaccessile build environments if possible
- Sexure the pipeline and how to modify it or its permissions
- Secure the git workflows that trigger build pipelines
-
-
Deploying CloudFormation
- Open the CloudFormation console
- CLick “Create Stack”, wiht “new resources”
- Click on “create template in Designer” <= you also can click on “Template is ready”
- Click on “template” bar, and there you can write your infra as a code in json format
- Once you copy your code in the template section, click “refresh” ( right top botton)
- Validate the template by clicking on the check mark on the top of the panel
- CLick upload
- CLick Next -> type a name for the stack -> click “next”
- CLick Next -> Click “create”
Now that the resource were created, to verify them:
- Click on “resources”
- Also you can see events, once all events are completed:
- Go to the selected resource console, for example SNS
- Look for the topic, click in topics. You should be able to find your topic there.
Here an example of how looks like a template:
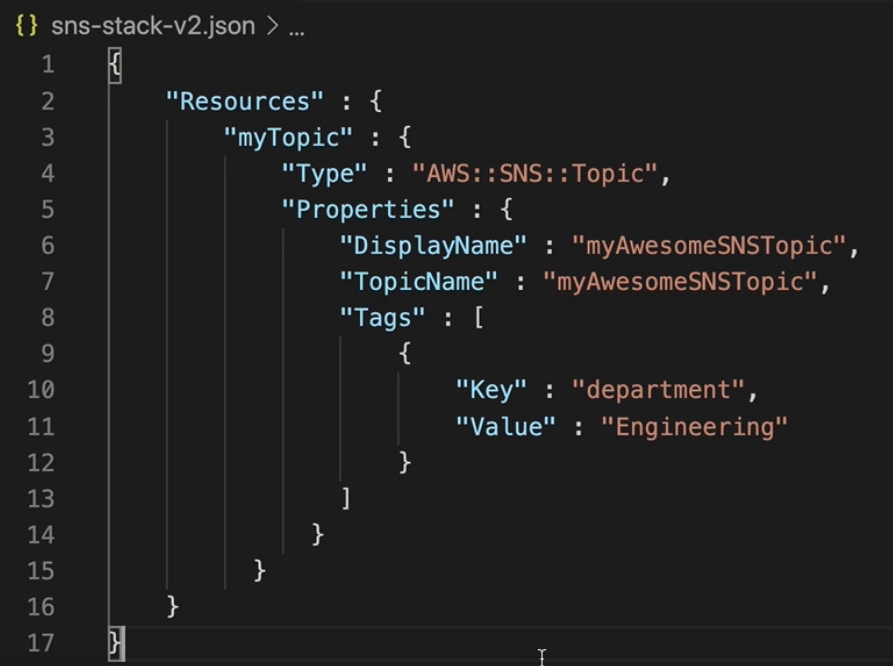
-
Deploying CloudFormatoin from CLI
# To deploy a stack $ aws cloudformation deploy \ --template-file myTemplate-stack.json \ --stack-name demoStack # To delete a stack $ aws cloudformation delete-stack \ --stack-name demoStack -
Parameter store in Lambda functions
# To create a parameter $ aws ssm put-parameter \ --name MyParameter1 \ --value Hello \ --type SecureString <== this means encrypted # To get the value of a parameter with an encrypted value $ aws ssm get-parameter \ --name MyParameter1 \ # To get the value of a parameter with an decrypted value $ aws ssm get-parameter \ --name MyParameter1 \ --with-decryption # TO update the value of the paramter $ aws ssm put-parameter \ --name MyParameter1 \ --value HiHi \ --type SecureString \ --overwrite -
Deploying parameters in Lambda function
# Create a stack with AIM capabilities $ aws cloudformation deploy \ --template-file myTemplate-stack.json \ --stack-name demoStack --capabilities CAPABILITY_IAM CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM <= allows you to use roles # To list Lambda functions $ aws lambda list-functionsIf the last command is too long, alternative way to find a specific is: - Open the Lambda console - Order the deployed lambda functions by “last modified”. Copy the name fo the lambda function
```bash # To retrieve the value of the lambda function $ aws lambda invoke \ --function-name XXXXASFASXZXXXXXX \ <-- name of the function copy from the lambda console result.txt <-- Will save output in a file ```
This is very useful if you want to hide secrets aways from your code or from being hardcoded
IV Building and testing
-
What is AWS CodeBuild
- CodeBuild automate building source code, execute test, and produce deployment artifacs.
- It is fully managed by AWS
- No build server is needed,
- No maintenance to build servers is required
- AWS offers pre-configurated environments.
- For different OS
- For different languages routines
-
CodeBuild concepts:
- It requires define a build project, which has the environment to build the source code: the build environment.
- It also requires define the buld specs. Specs show the specific process to execute the build.